As we age, our bodies undergo various changes, including alterations in blood sugar regulation. For the elderly population, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can be a concerning issue that requires careful management. In this blog, we will explore six practical strategies to help keep low blood sugar at bay, ensuring older individuals’ well-being and quality of life.
1) Balanced Meal Planning
Maintaining a well-balanced diet is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. Encourage older people to eat regular meals and snacks throughout the day, ensuring that each meal contains a combination of complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid excessive consumption of refined sugars and opt for whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins instead. Encourage portion control to prevent overeating or consuming too few carbohydrates. Regular meals help stabilize blood sugar levels and provide a steady energy supply.
2) Consistent Carbohydrate Intake
Monitoring carbohydrate intake is pivotal for individuals with low blood sugar. Encourage older people to consume consistent carbohydrates with each meal or snack. Opting for slow-releasing carbohydrates, such as whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables is advisable. These options provide sustained energy and help prevent blood sugar fluctuations. Also, encourage individuals to avoid skipping meals or snacks, as this can lead to low blood sugar episodes.
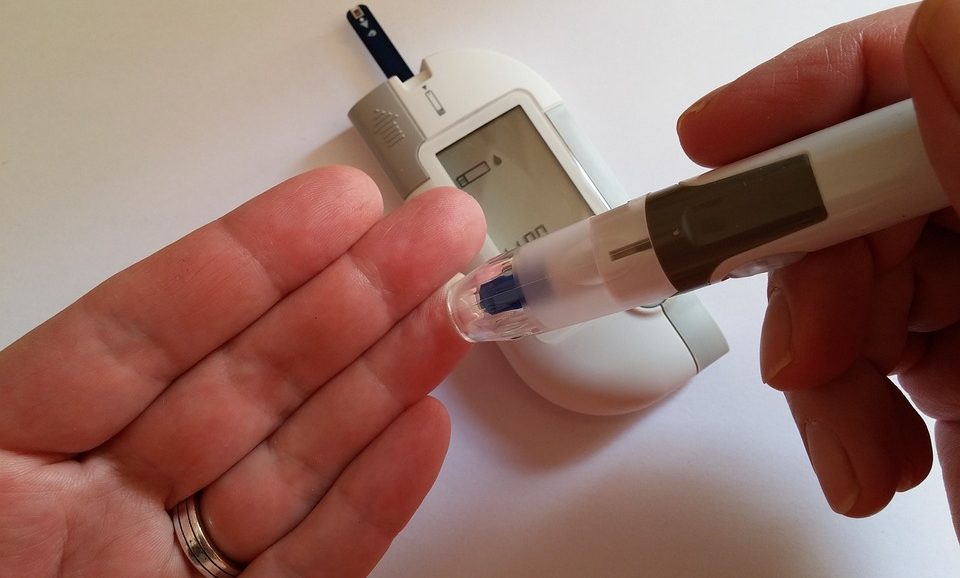
3) Frequent Monitoring
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for managing low blood sugar effectively. Encourage older people to work with their healthcare provider to establish a monitoring schedule suitable for their needs. Teach them how to use a blood glucose meter, record their readings, and understand the target range. Monitoring blood sugar levels allows for timely intervention if levels drop too low, enabling individuals to take appropriate steps to raise their blood sugar levels to a safe range.

4) Medication Management
For elderly individuals with diabetes or other conditions requiring medication that affects blood sugar, adherence to medication schedules is vital. Help them create a system to ensure timely medication intake and assist in organizing pillboxes if necessary. Remind them of potential side effects of medications, including low blood sugar, and encourage them to seek medical advice if they experience any concerning symptoms. Regular communication with healthcare professionals can help optimize medication management and prevent complications.
5) Physical Activity and Exercise
Regular physical activity plays a significant role in managing blood sugar levels. Encourage the elderly to engage in suitable exercises according to their abilities and medical conditions. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or light strength training can help improve insulin sensitivity and maintain a healthy weight. Remind them to check their blood sugar levels before and after exercise to understand how their body responds. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals before starting any new exercise regimen.
6) Emergency Preparedness
In the event of low blood sugar, the elderly and their caregivers need to be prepared. Encourage them to carry a quick-acting source of glucose, such as glucose tablets or a small juice box, at all times. Make sure family members and close friends are aware of the situation and understand the necessary steps to take in case of an emergency. Prompt treatment can prevent complications and ensure the safety of the elderly individual.
Managing low blood sugar in the elderly requires a holistic approach that encompasses dietary modifications, regular monitoring, medication management, exercise, and emergency preparedness. By implementing these practical strategies, older individuals can enjoy better blood sugar control, improved overall health, and enhanced quality of life in their golden years.
Let us know if these few tips have helped you and drop your tips in the comments below!